There aren’t many things that spark as much interest throughout the media landscape as the release of a new version of DaVinci Resolve, and this was something we were recently treated to with the launch of Resolve 18 by Blackmagic Design. As always, this powerful NLE comes equipped with an array of very innovative tools and features and you can read all about these in our latest blog on the new product launch. Here though, we’ll examine the new Depth Map effect in greater detail.
Why a Depth Map?
In color grading, it is often the case that the background requires color enhancements and changes that do not need to be applied to the foreground. The opposite is also often the case, especially in interview situations. The new Depth Map effect allows you to generate a 3D depth matte of a scene automatically and makes it possible to quickly grade the foreground separately from the background, and vice versa.
This new effect saves a lot of time as it essentially replaces the need for masking and rotoscoping objects by hand, often in a tedious frame-by-frame process. The creation of this virtual depth map from a 2D scene is done by the DaVinci Neural Engine and is actually quite fast and precise. The Depth Map can effectively be used like any mask in Resolve to display or remove any effect, not just color grading results.
Using the Depth Map effect
This effect can be applied via the Edit page or the Color page and it can be found in the Effects Library under Open FX. While on the Edit page, a simple double-click on the Depth Map effect will apply it to the selected clip. To apply the effect on the Color page, drag-and-drop the Depth Map node from the Effects Library into the Node window.
Adding the effect to a clip on the Edit page will use the Depth Map to mask the clip while adding it in the Color page will mask the downstream color settings and effects.
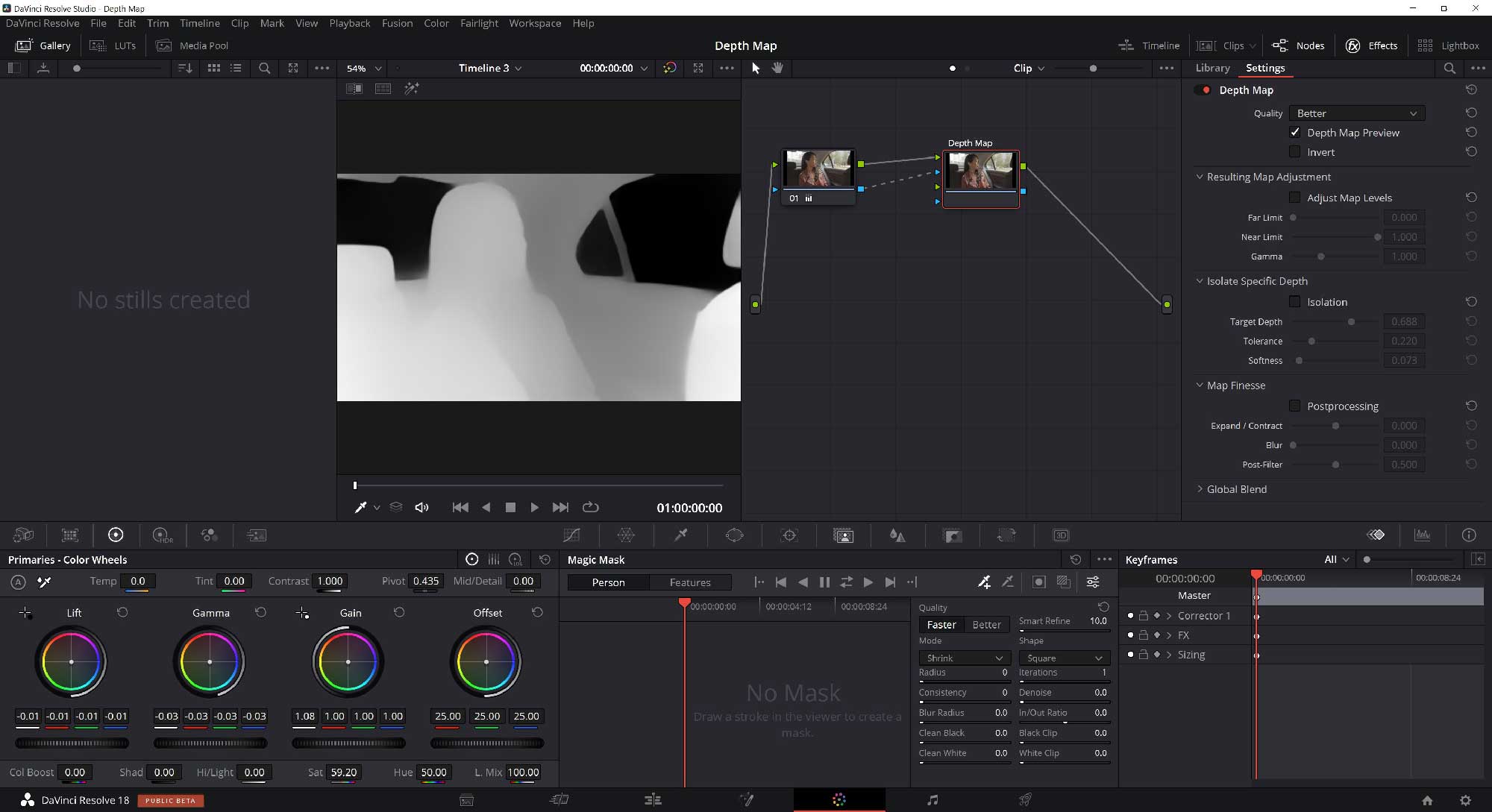
When the Depth Map effect is added to a clip, Resolve uses the DaVinci Neural Engine to analyse the video and automatically create an alpha channel where black areas represent transparency and the white areas opaqueness. It takes just a few seconds for a Depth Map to be created. With the default settings, the objects closer to the camera will be more opaque while the objects in the background will gradually become more and more transparent. This can easily be flipped using the invert function. The effect works really well in separating different depths in the picture. The user can adjust map levels in the Resulting Map Adjustment menu where both near and far limits can be set, and the gamma value adjusted. These adjustments shift the map focus and allow the user to better set which parts (or depths) of the scene should be keyed in or out.

The user can also increase the contrast of the map in the Isolate Specific Depth menu and thereby reduce the map to a certain depth. This function is helpful when trying to isolate the subject in a scene and will be more or less effective depending on the scene – the more the subject is separated from the background the better. To finely tune the edges of the map Resolve provides the Map Finesse menu.
Apart from color grading, the Depth Map effect can be used to create an alpha channel for applying effects selectively. This can be useful in bringing the background out of focus during post-production or when adding creative effects such as 3D titles.

Find out what else is new in DaVinci Resolve 18
Struggling with the performance of DaVinci Resolve? Read this blog about 5 ways to achieve better playback performance.